Functional Disorders
Functional disorders are those disturbances in which the bowel looks otherwise normal but functions improperly. These types of problems are common and include a variety of manifestations such as diarrhoea, constipation, abdominal pain, fullness sensation and indigestion.
It is not certain what causes a functional disorder but 60 percent of all such patients have associated disorders such as depression or anxiety, highlighting the “gut-brain” connection.
Functional GI problems most commonly affect the colon and rectum, and includes leaky gut syndrome, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), along with constipation and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
1. Constipation
Constipation is the difficult passage of stools (bowel movements) or the infrequent (less than three times a week) or incomplete passage of stools. Constipation is usually caused by inadequate “roughage” or fibre in the diet, or a disruption of the regular routine or diet.
Constipation causes a person to strain during a bowel movement. It might include small, hard stools, and sometimes causes anal problems such as fissures and haemorrhoids. Constipation is rarely the sign of a more serious medical condition.
Treatment of constipation includes increasing the amount of fibre you eat, exercising regularly, and moving your bowels when you have the urge (resisting the urge causes constipation). If these treatment methods don’t work, laxatives are a temporary solution, since the overuse of laxatives can actually aggravate symptoms of constipation and cause permanent damage to the bowels
2. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)

Irritable bowel syndrome (also called spastic colon, irritable colon, or nervous stomach) is a condition in which the colon muscle contracts more readily than in people without IBS. A number of factors can trigger IBS including certain foods, medicines, and emotional stress.
Symptoms of IBS include abdominal pain and cramps, excess gas, bloating, and a change in bowel habits such as harder, looser, or more urgent stools than normal. Often people with IBS have alternating constipation and diarrhoea.
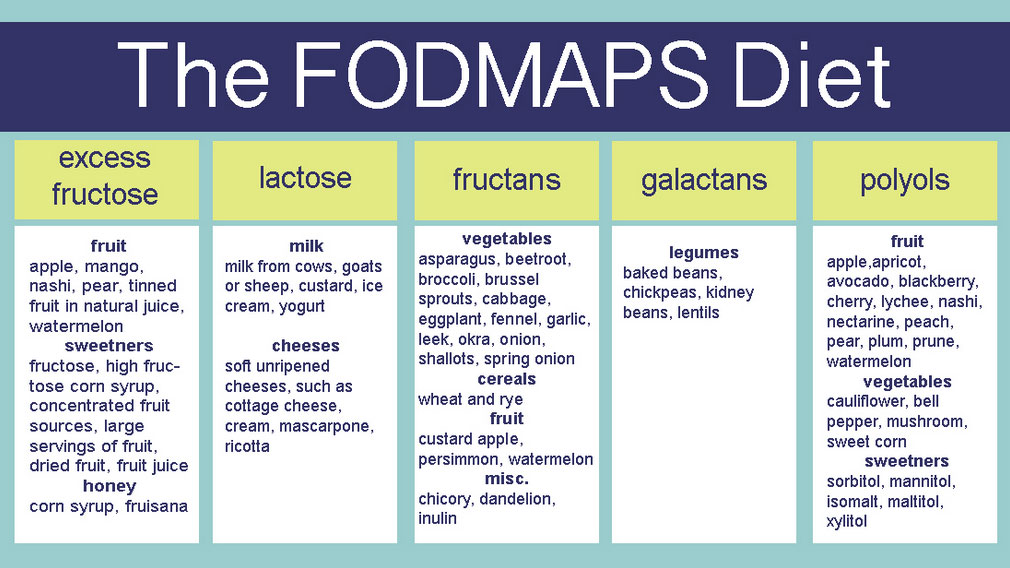
Treatment includes avoiding caffeine, increasing fibre in the diet, monitoring which foods trigger IBS (and avoiding these foods e.g. FODMAPs diet), minimizing stress or learning different ways to cope with stress, and sometimes taking prescribed medicines.
FOODS TO AVOID ON THE FODMAPs DIET
FODMAP is an acronym for :
- Fermentable
- Oligosaccharides (eg. Fructans and Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Disaccharides (eg. Lactose)
- Monosaccharides (eg. excess Fructose)
- And
- Polyols (eg. Sorbitol, Mannitol, Maltitol, Xylitol and Isomalt)