MTHFR Gene Defect
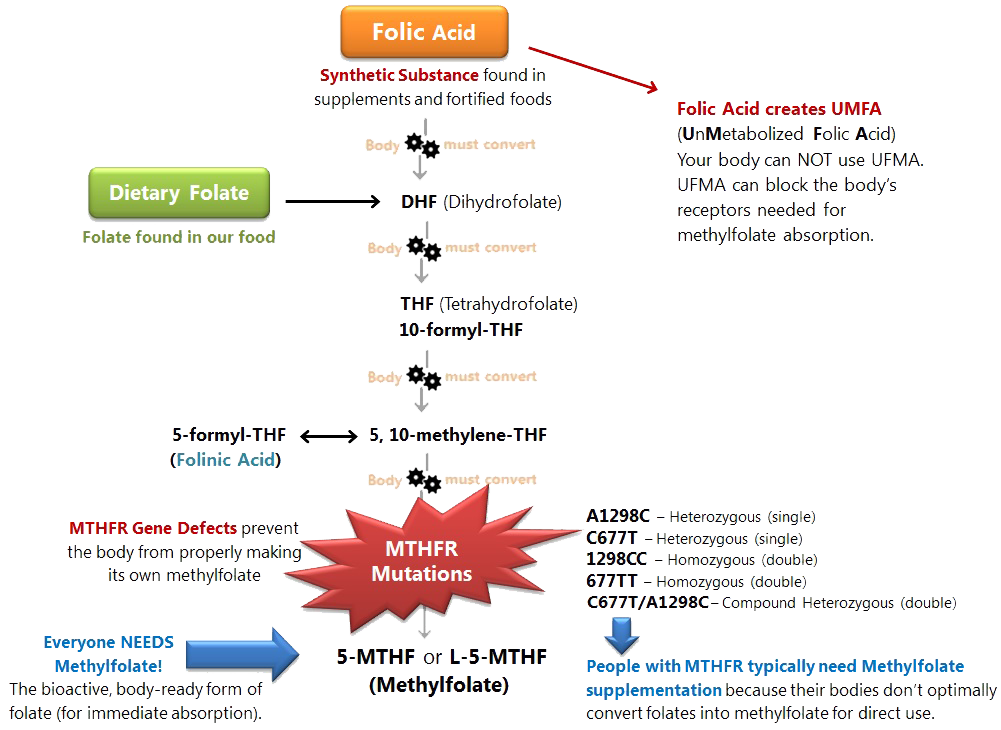
MTHFR (methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase) is an enzyme that converts dietary folate (commonly known as folic acid or B9) into the active form 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF or L-methylfolate).
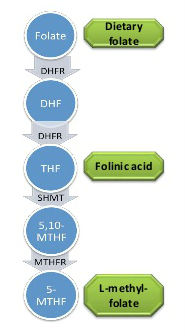
L-methylfolate is needed for many essential body processes, including the manufacturing of the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine. Deficiency in L-methylfolate can not only cause depression, but it can create the type of depression that is resistant to other treatments until the deficiency is corrected.
Mutation or defect in the MTHFR enzyme affects how much active folate becomes available. This can also make it more difficult to break down and eliminate synthetic folic acid (common in many multi-vitamins), along with other substances like heavy metals and environmental toxins.
Folate is required for the following:
- Optimal cell health and energy production
- Methylation reactions (for the creation of every cell in the body, with methyl groups being the ‘on-off’ switches of cellular activities)
- Amino acid metabolism (for serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline production & detoxification)
- Formation & maturation of RBC, WBC and platelets
- Detoxification of homocysteine (nutrient deficiencies in folate, B6 and B12 have been associated with elevated homocysteine)
Researchers believe that up to half of the population may carry this defective gene. If found to be present, it can easily be treated by using L-methylfolate supplementation.
Hence, methylation is a vital pathway for good health, energy and well-being. The main known causes of under-methylation and elevated homocysteine are a dietary deficiency of vitamin B12, B6, folate or an inbuilt inability to manufacture L-methylfolate due to the MTHFR gene mutation.
THE METHYLATION CYCLE
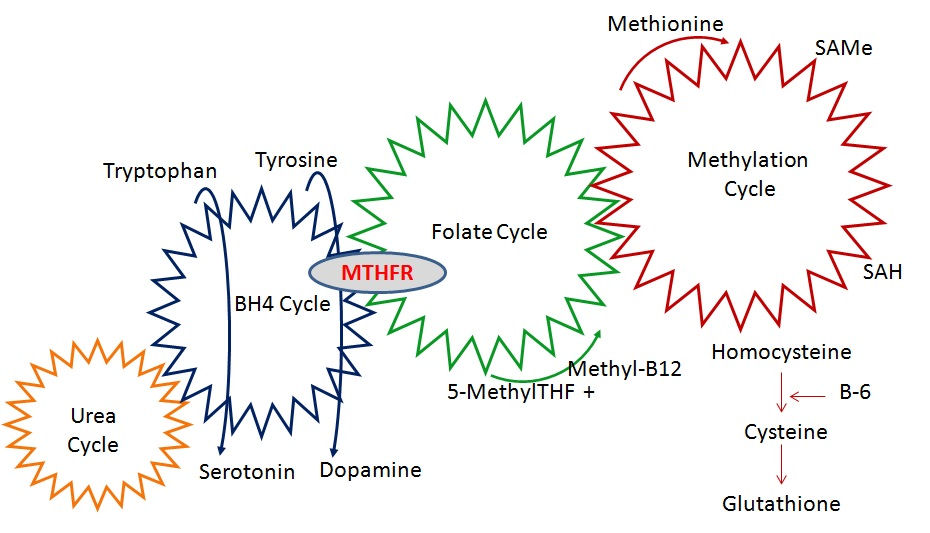
However, in addition to the MTHFR gene, there are a multitude of genes involved in the methylation pathway. Many people can’t cope with supplementation initially as the body may have issues in other areas and pathways (e.g. inflammation, gut health, detoxification or hormonal balance). Introducing L-methylfolate to the body whilst these issues are still occurring can lead to side effects and/or making symptoms worse, so it is advisable to work with a practitioner who is familiar with methylation.
Mood symptoms of an underlying gene mutation like the MTHFR mutation can include:
- Lingering fatigue
- Fogginess & forgetfulness
- Sleep issues
- Mood swings
- Anxiety & irritability
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Autism
- ADHD
Stress is a compounding factor.
Other significant gene mutations connected with depressive disorders include APOE, DRD4, GNB3, SLC6A3 and SLC6A4.
I share this information to educate you on the “biochemical nature” of your body and how it processes information, but as you may have noticed, it is highly related to the foods you eat, the lifestyle you lead, and even your genetic makeup.
Incorporating specific diet and lifestyle changes based on the underlying cause of your mood disorder, can create much better health in your mind, your physical body and even your spirit.
CLICK HERE for consultations with me….
