
Hair is one of the first things people notice about us when we meet them. Hair conveys aspects of your style and personality.
I have always had thick hair and I must admit I have taken it for granted – well until now. Seeing strands of hair on my hands after simply stroking my curls, noting hair bundles on my clothes throughout the day and excessive hair loss in the shower drain have sent my alarm bells ringing.
I am not alone with this issue I can tell you now. There are many women fearful of simply touching their scalp as I type.
So what is happening really?
Not a simple answer sorry. There are so many factors that need attention – luckily we have lots of tools to restore balance to our bodies.
So let’s journey together once more.
Hair loss in women is a common problem, especially during menopause. It can be distressing and negatively affect self-esteem, but there are many strategies and treatments to manage hair loss in women.
The medical term for baldness is alopecia. Complete baldness of the scalp is alopecia totalis. Continue reading to learn more about what causes hair loss in women and about treatment strategies. You’ll learn that some types of hair loss in women are temporary, while others may be permanent and require treatment. Reasons for hair loss in women are varied and many.
Hair Loss in Women
We think of hair loss as a common problem in men, but women experience it too. Fewer than 45% of women go through their whole lives with a full head of hair. What causes hair loss in women? Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is a common cause and it increases with advancing age. This type of hair loss may begin in a woman’s 40s, 50s, or 60s. It is hereditary and genes inherited from the mother, father, or both may contribute to the condition. Women who experience hair loss often experience psychological distress and impaired social functioning as a result of it. As female pattern hair loss tends to be a chronic, progressive condition, early diagnosis and treatment are critical. This may help arrest subsequent hair loss.
Some treatments may even help stimulate the growth of new hair. See your dermatologist if you are experiencing hair loss. Stopping hair loss in women is possible depending on the cause and how soon the problem is identified. Early treatment may slow or reverse hair loss in women. A trichologist is a dermatologist who specializes in the health of the scalp and hair.
How Hair Grows
If you’re wondering what to do about hair loss in women, it makes sense to first understand how hair grows. The human scalp contains about 100,000 hair follicles. Hair grows from the bottom of the follicle from an area called the root. Blood vessels nourish the root, allowing hair to grow. Hair grows up and toward the skin, passing an oil gland. Oil glands keep hair shiny and soft. Too much oil may make hair greasy.
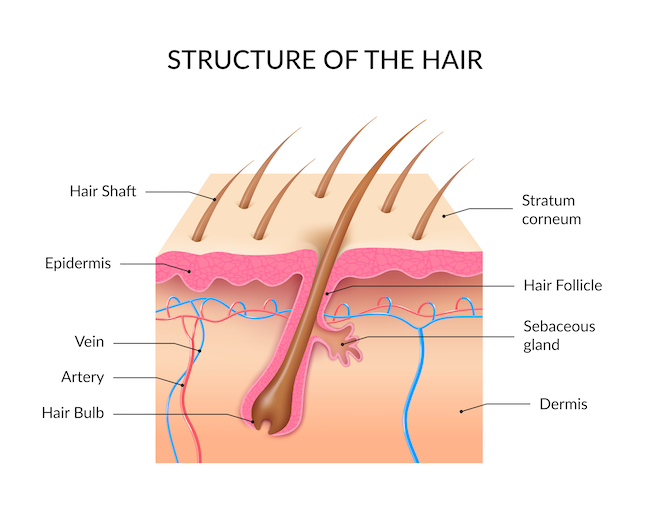
Hair is dead by the time it pokes out through the skin. Hair on the head grows at a rate of about half an inch per month. Hair on your head remains there for between 2 to 6 years. That is about the length of time for the growth phase. Then the hair stops growing for a period before it falls out. The resting phase of the hair follicle is called the telogen phase. Then the cycle begins anew.
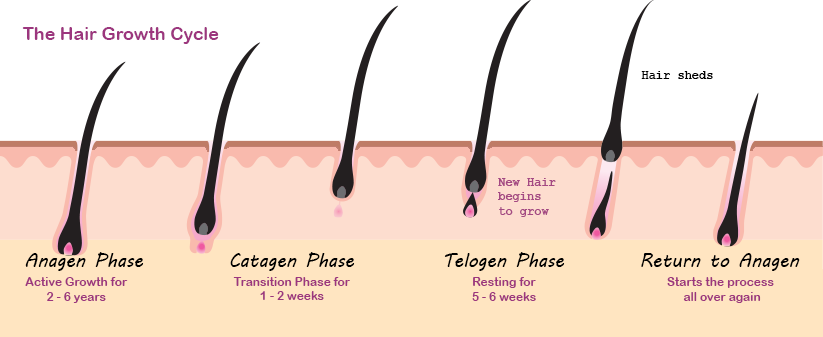
Is Hair Loss Normal?
We all lose hair. Some hair loss is perfectly normal, as hair falls out after it completes the 2 to 6-year growth phase. You may notice loose hairs that have fallen out on your clothes or in your comb or hairbrush. The average person loses about 50 to 100 hairs per day. This is normal. What is not normal? Excessive hair loss in women may be apparent by the following: If your hair starts to fall out in clumps, especially when you brush or comb it or are in the shower, you should see your doctor. If you notice that you can see larger areas of your scalp or that your hair is thinning, see your dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment of your hair loss condition.
What Causes Hair Loss?
There are many different types of hair loss with a variety of potential underlying causes. Several medical conditions are associated with hair loss in women. Common causes include thyroid problems and hormone imbalances. When the underlying cause of hair loss is diagnosed and treated, hair loss may stop and hair may grow back. Stress, nutritional factors, and genetics may also play a role in hair loss. Severe physical stress such as going through childbirth, surgery, or suffering a serious illness may precipitate a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. This is a condition in which stress forces large numbers of follicles to enter the resting phase, and after a few months, hair will fall out.
Sometimes doctors are not able to determine what is causing hair loss. Other potential causes of hair loss include radiation therapy, cancer, kidney failure, liver failure, medication side effects, and autoimmune disease. If you are experiencing new or increasing hair loss, see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
How Do You Measure Hair Loss?
Doctors characterize the severity of hair loss using something called the Savin density scale. This scale has various stages and describes hair loss around the midline part as well as recession in the front of the hairline. Some women lose hair to various degrees around the midline and/or in the front of the hairline. Some women experience hair thinning all over the scalp. Hair loss may occur in episodes or continuously. The doctor parts the hair down the middle of the head and then determines the severity of hair loss. The most common pattern for female pattern baldness is thinning around the midline that occurs in the shape of a Christmas tree. The pattern and severity of female hair loss helps determine the appropriate course of treatment.

Grade 1
This is described as minimal thinning, which can be camouflaged using different hairstyling techniques. Hair loss at this stage may be so slight that it goes unnoticed. Typically, at this stage, a woman’s hair will appear thinner, but the front hairline does not recede.
Grade II
This stage is considered moderate hair loss. Women in this category may notice decreased volume and a widening of their part. More of the scalp may become visible and an increase in shedding may be noticeable.
Grade III
Often described as diffuse thinning, this type of hair loss creates a see-through appearance on the top of the scalp. This is the rarest, most severe type of hair loss for women and it’s difficult to mask with hairstyling techniques.
Possible Causes
The Thyroid Disease Connection
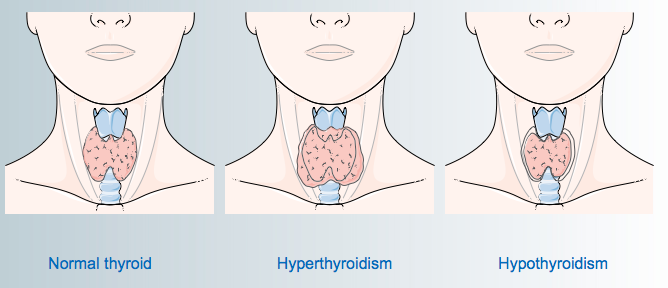
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that rests in the front base of the neck. It secretes thyroid hormones that are used by every cell in the body. There’s a connection between hair loss in women and thyroid disease. Imbalances in thyroid hormone levels are a common reason for hair loss in women. Too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism) and too little thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) may both trigger hair loss. Other symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, rapid heart rate, inability to fall asleep or stay asleep, and anxiety. In addition to hair loss, hypothyroidism may be associated with weight gain, fatigue, feeling cold, slow heart rate, and constipation. Luckily, thyroid hormone imbalances are easily detectable with blood tests. Treatment helps alleviate symptoms, including hair loss.
Recent Illness
Recovering from any infection really takes a toll on the immune system and fast-growing cells like hair, skin, and nails are often neglected as the immune system steers towards more ‘important’ organs to aid in the complete expulsion of the parasite creating the disease state.
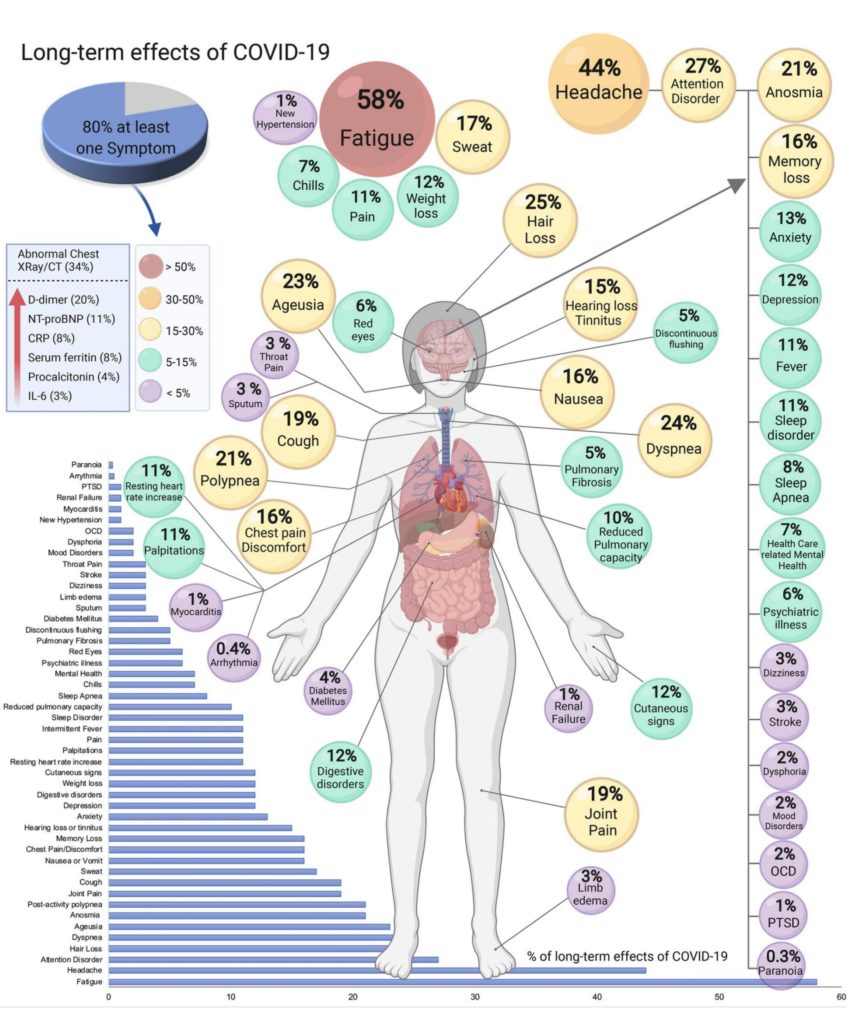
For instance, the COVID-19 virus affects people in many different ways and can have some long-term effects, including hair loss (telogen effluvium). In fact, 25% of long-haul sufferers experience hair loss in addition to many other symptoms post-infection.
PCOS Can Be a Trigger
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in women in which the body manufactures more androgens or male hormones than it normally should. It is a potential cause of hormonal hair loss in women. Women who suffer from this condition may grow facial hair and extra body hair. One of the other symptoms of this condition is thinning of hair on the head. Women affected with PCOS may also experience weight gain, acne, menstrual cycle irregularities, ovulation problems, depression, and infertility. Hair thinning may be the only outward sign that a woman is suffering from this condition.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is a condition that causes hair loss in round patches on the scalp and body. Alopecia is the medical term for baldness. With alopecia areata, missing hair often grows back approximately 6 months to 1 year later. Less than 5% of people lose all the hair on their head and body. Complete baldness of the scalp is called alopecia totalis. This type of hair loss is not contagious. What causes alopecia areata? It is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks and destroys hair follicles. Hair loss due to alopecia areata tends to come on suddenly.
The condition may be treated with steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, or immunosuppressive medications. People with alopecia areata suffer from more allergies, asthma, and autoimmune conditions compared to those who do not have the condition. Minoxidil (Rogaine) for hair loss in women is one option for treatment.

High Levels of DHT
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a sex hormone that’s naturally produced in the body and plays a major role in developing certain masculine characteristics such as the prostate, muscle growth, deep voice, and hair. This hormone is a modified form of testosterone. Despite the fact that most people don’t have to worry about their DHT levels, excessive levels of this hormone can cause hair loss. High levels of DHT block essential nutrients from reaching the hair follicles, which causes hair to degrade, shrink, and eventually stop growing thus leading to baldness.
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies
There are many deficiencies that can lead to hair loss. One reason is folate deficiency. Your immune system needs a lot of folate to make new red blood cells- especially folinic acid (NOT folic acid which is synthetic). The growth of hair also requires a lot of folate for cell division and growth. If your immune system uses the majority of your folinic acid, your hair is left with very little. The result? Your hair becomes undernourished and falls out. Folate and vitamin B12 work well together so it’s best to support with a combination of both.
Low ferritin levels (the form of iron stored in the liver as a reserve supply) are also a major reason for hair loss. Levels below 70ng/mL can lead to thinning hair and levels below 40ng/mL are commonly associated with hair loss.
Biotin (also known as vitamin B7) is also vital and problematic if deficient. It stimulates keratin production in the hair and can increase the rate of follicle growth.
Zinc plays an important role in hair tissue growth and repair. It also helps keep the oil glands around the follicles working properly. Hair loss is a common symptom of zinc deficiency.
A number of symptoms, such as hair loss, can occur when your body lacks the recommended amount of vitamin D. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to alopecia.

Ringworm and Hair Loss
Ringworm is a fungal skin infection that causes patches of hair loss. The official medical name for ringworm on the scalp is tinea capitis. The infection starts out as a small pimple that grows larger. Affected areas are itchy, red, inflamed, scaly patches with temporary baldness. The skin may ooze. People may have one or more bald spots. Ringworm is more common in children, but adults can get it, too.
The fungus triggers hair loss by causing hair to become brittle and break off. The skin often appears most red around the edge of the lesion, with a more normal-appearing skin tone in the center. That is one of the reasons the condition is called ringworm. The condition is contagious with skin-to-skin contact. It is also transmissible by infected combs, hairbrushes, unwashed clothing, and surfaces in gyms, showers, and pool areas. Your doctor can treat ringworm with oral antifungal medication. Ringworm on the scalp is one potential cause of hair loss in women that is reversible.
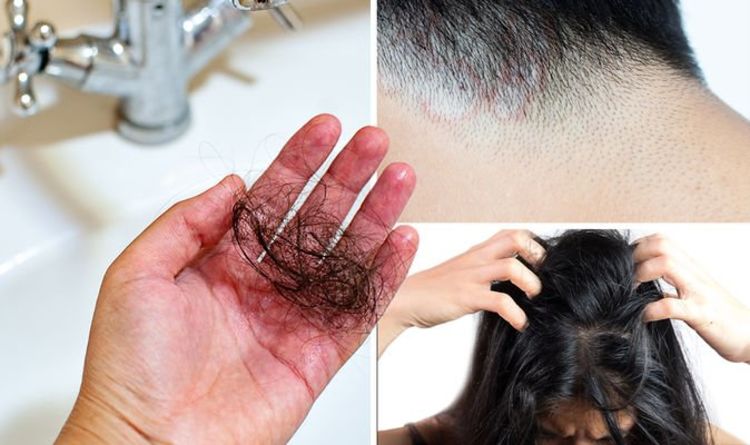

Childbirth May Be a Trigger
Moms-to-be are often very happy that their hair seems much fuller during pregnancy, but they are then disappointed when they experience hair loss after giving birth. Losing hair after pregnancy is not true hair loss and is normal. That’s because hormones and hair loss in women are linked. Hair falls out after women give birth due to decreasing estrogen levels. Some women notice that they lose a lot of hair in a short period of time after giving birth. The good news is that after this shedding period, hair fullness often returns to normal within 1 to 2 years. Many people wonder what’s the best treatment for hair loss in women. For postpartum moms waiting for their full head of hair to return, using over-the-counter volumizing shampoo and conditioner formulated for fine hair can make the hair appear fuller.
Mindful of Birth Control Pills
Birth control pills are a form of contraception that works by suppressing ovulation and/or making it more difficult for a fertilized egg to implant into the lining of the uterus. Hormonal hair loss in women may occur when women start or stop taking certain kinds of contraceptives. The hormones that make birth control pills effective may also cause hair thinning in women who use them. You are more likely to experience this side effect from birth control pills if you have a family history of hair loss. Stopping the pill is also a cause of hair loss in women. Hormones are not the only medication that may be associated with hair loss. Blood thinners and blood pressure medications may do it too. Drugs that treat depression, heart disease, and arthritis can also be an issue.
Crash Diets Are Dangerous
Crash diets and fad diets promise quick weight loss, but most do not work and can be dangerous. If you lose 15 pounds or more very quickly, you may lose a significant amount of hair within a matter of months. Inadequate protein and nutrients are some of the potential reasons for hair loss in women. Stick to a healthy, balanced eating plan. Fresh fruit, vegetables, lean meats, and complex carbs give your body the fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals you need to maintain a healthy body, including a full head of hair.

Style Hair Carefully
Wondering what to do about hair loss in women? Loosen up! Tight ponytails, hats, scarves, cornrows, and bandannas can all pull on the hair and lead to hair loss by a process called traction alopecia. The gradual, constant tension irritates the scalp and may cause hair to fall out. Ditto for tight rollers. One of the potential solutions for hair loss in women is to wear your hair down to eliminate tension. Your hair should grow back if traction alopecia was to blame for losing your locks. Beware especially of long-term use of tight hairstyles. These may scar your scalp and lead to hair loss that is permanent.
Be wary of chemicals in hair colouring products also since they are known to cause scalp reactions and damage hair. Seek to use a more gentle and natural colouring brand instead.
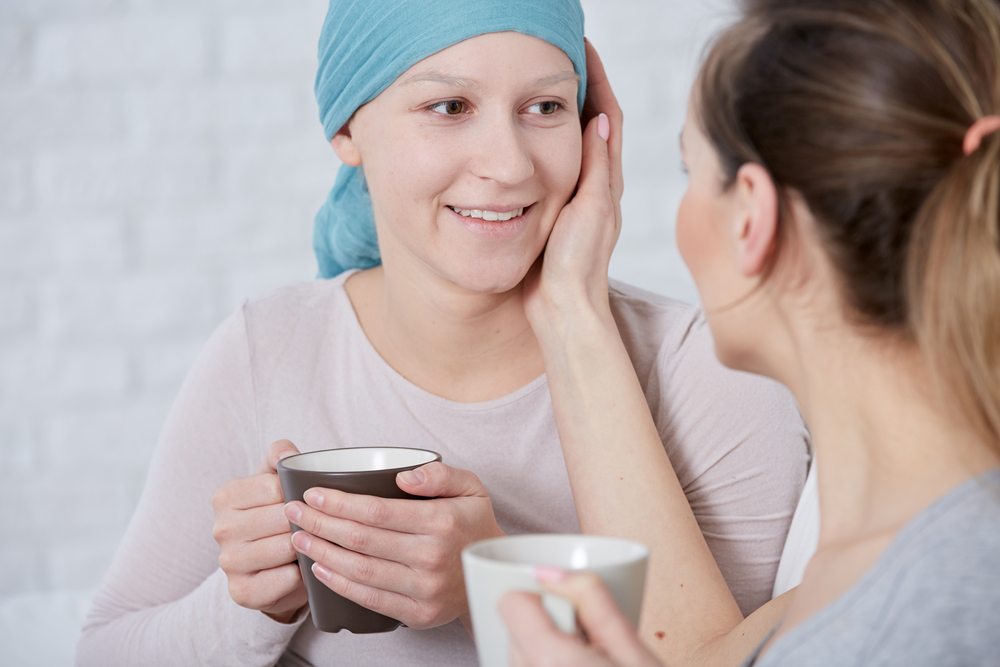
Cancer Treatment Is a Trigger
Radiation and chemotherapy used to treat cancer are some of the common causes of hair loss in women. Both therapies harm hair follicles in addition to killing cancer cells. People undergoing cancer treatment often experience dramatic hair loss as a result of these therapies. They may wake up with clumps of hair on their pillow or they may lose large amounts of hair in the shower. Rapid hair loss in women often starts within 2 weeks of beginning treatment. It may be worst between 1 to 2 months into therapy. The scalp may be extra sensitive during this time. It may be irritating to wash, brush, and comb hair. The good news is that once cancer treatment is over, hair tends to grow back.

Physical and Emotional Stress
Extreme physical or emotional stress may trigger sudden hair loss in women. Hair loss due to physical or emotional stress is called telogen effluvium. Circumstances that may precipitate this pattern of hair loss include serious illness or injury, surgery, severe emotional upset, blood loss, and weight loss. Sometimes a reaction to medication may trigger this kind of hair loss. Telogen effluvium may last for 6 to 8 months before resolving.
Treatments
Medication for Hair Loss
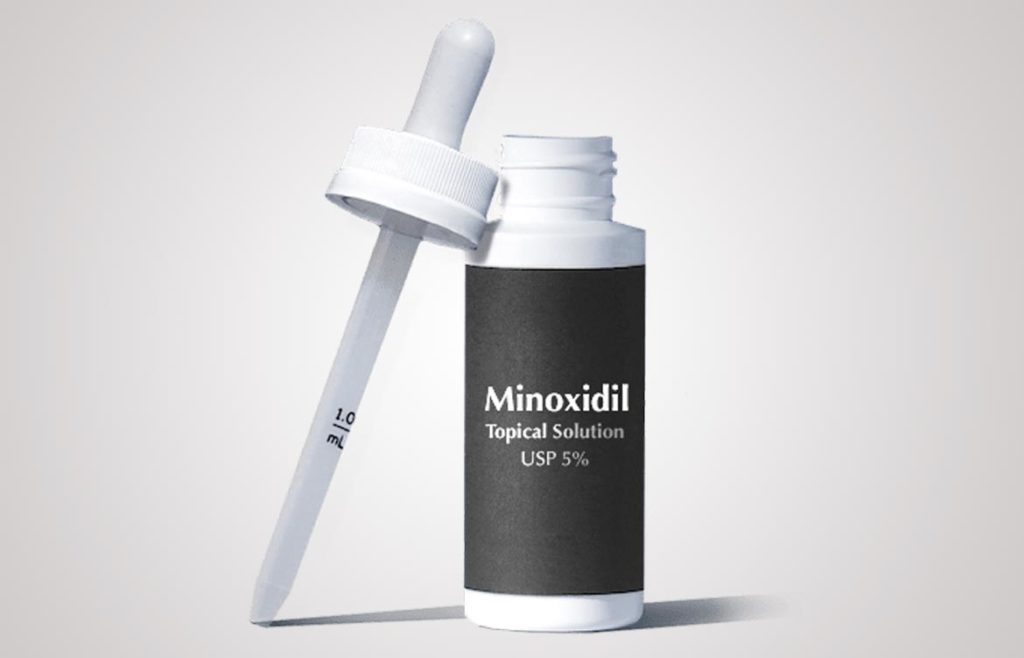
1. USE 5AR INHIBITORS
5AR Inhibitors prevent the body from converting testosterone to DHT. Medications such as Dutasteride, topical/oral Minoxidil, and Finasteride are approved by medical professionals to treat male pattern baldness.
Minoxidil, or Rogaine, is a topical medication that is used to treat female pattern hair loss and male-pattern baldness. It was initially developed as a blood pressure medication and was used off-label to treat hair loss until it became FDA-approved for that purpose. Minoxidil can slow the progression of hair loss. Most women who use the medication experience regrowth of hair. The medication needs to be used continuously to maintain results. Compounded minoxidil can be used orally also.
Other types of treatment work for different kinds of hair loss. Corticosteroids help suppress the immune response that damages hair follicles in people who have alopecia areata. Once the follicles recover, hair can grow back. If nutritional deficiencies underlie hair loss, eating a healthy diet with adequate protein and nutrients can help you regrow hair. Certain medical problems may trigger hair loss. Adequately treating these conditions may help restore hair growth.

2. HERBAL DHT BLOCKERS
The herbal route is also an effective natural way to reduce DHT in the body. Some of the herbal DHT blockers include nettle leaf, pygeum bark, green tea, fenugreek, reishi, and saw palmetto.

3. DHT BLOCKER SHAMPOO
Using the right shampoo and conditioner can also help to block DHT, wash away excess sebum, and support healthy hair. Make sure your shampoo is sulfate-free and contains topical DHT blockers such as ketoconazole, tea tree oil, and lavender.
Shampoos should be sulfate-free because sulfates are harsh and drying which can worsen hair loss.
Even if you use a sulfate-free shampoo you should condition your hair after shampooing to restore moisture and reduce dryness. Using a conditioner with jojoba oil as it is chemically similar to natural oils produced by the skin.

4. SUPPLEMENTS
Correcting known deficiency states is vital to halting hair loss.
Nutrients important for healthy hair include protein (especially l-lysine), collagen, B vitamins (including B7/ biotin, B9/folinic acid, and B12/hydroxy version best), vitamins A, C, and D, and minerals like iron, selenium, calcium, and zinc.
Whether you’re looking to strengthen your hair, skin, or nails, collagen is the way to go. Collagen has plenty of antioxidants, promotes healthy hair roots, and can increase the production of fibroblasts (which increase collagen production in the body).
Collagen contains 3 nonessential amino acids: proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline. Although the word “nonessential” can make us believe we don’t need those amino acids, what it actually means is that our body can produce them naturally. Along with keratin, collagen gives hair its shape and elasticity. A collagen deficiency can be especially damaging to women who have started to see signs of hair loss. It makes the hair brittle and more prone to shedding.
The added boost of proline from collagen supplements essentially provides the necessary tools for our body to construct keratin and build up healthier hair.
Studies also suggest that the decrease in estrogen as women age is directly tied to the decrease in collagen production. So, collagen is wonderful for menopausal women.
The role of the essential amino acid, l-lysine, in hair loss also appears to be important. L-lysine helps the body absorb iron (known for hair loss) from the food you eat, nourishing your hair follicles and encouraging growth. L-lysine has been shown to make the natural DHT blockers in your body more effective. The more DHT your body is able to fight off, the better able you will be to fight off hair loss.
L-lysine helps the body form collagen, one of the most important proteins for hair. L-lysine doesn’t create collagen itself. Instead, it helps your body create and absorb calcium, a vital nutrient needed for collagen production.
Calcium is a vital nutrient for collagen production. When your body is low on calcium, your hair becomes dry and brittle. About 75% of people are calcium deficient, meaning that their hair health suffers even more.
The amount of calcium you need changes over time. As you get older and hair naturally starts to thin, better calcium absorption can help fight against hair shedding. This is especially important if you’re a coffee drinker – caffeine is a natural calcium blocker.
As a precautionary note, over-supplementation of certain nutrients, including selenium, Vitamin A, and Vitamin E, has actually been linked to hair loss. So check with your practitioner first before self-prescribing to be sure you actually need to supplement.
Laser Therapy
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a treatment that may help regrow hair and reverse hair loss in women. The lasers are available for home use and in doctor’s offices. Laser therapy must be used for between 2 to 4 months before results are visible. Laser therapy is an alternative to medication and hair transplant surgery. The devices are approved by the FDA, but the approval process for devices is not as stringent as it is for medications that undergo a rigorous clinical trial process. Long-term safety and efficacy data for low-level laser therapy are not available. Laser therapy may be effective for 50% of men over the age of 40 and 75% of women over the age of 65 who suffer from certain kinds of hair loss.
Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure in which a doctor removes hair from part of the scalp and transfers it to areas of the scalp where it is thinning. In cases of female pattern hair loss, hair may be thin all over, so it may be difficult to find adequate donor sites for harvesting hair. Hair transplantation is more effective for those who suffer from male pattern baldness or those who suffer from thinning of the frontal scalp. Patients may need multiple sessions to achieve desired results.
Chemical Stimulation
This requires those experiencing baldness to apply a mixture of hair-growing ingredients such as peppermint essential oil, rosemary essential oil, emu oil and pumpkin seed oil, which act as DHT blockers to their scalp. Doing this is said to improve hair growth and blood circulation on the scalp. In fact, several trials suggest that rosemary oil is just as effective as minoxidil in preventing hair loss and encouraging new hair growth.

Exfoliation
Cleansing the scalp is one of the simplest, natural ways to curb the frustrating effects of DHT on the scalp. Exfoliation involves removing any present build-up from the scalp while cleaning. Dead skin and excess sebum on the scalp that may clog the pores are also cleaned.
Diet
Diets low in calories or fat are linked to weak, unhealthy hair. So it’s vital to eat a well-balanced diet of protein, fat, carbohydrates, and fibre.
There are several foods that are natural DHT blockers. For instance, vegetable foods rich in zinc contain phytosterol, which blocks DHT production and reduces areas on the scalp and hair follicles where DHT can attach itself. These foods include spinach, white mushroom, kale, etc. Foods rich in lycopene such as tomatoes, watermelons, apricots, grapefruits, guava, carrots, and mangoes naturally block DHT production.
Caffeine is also a DHT blocker which is wonderful news for all the coffee lovers out there, but just keep in mind it interferes with the absorption of many vital nutrients that can lead to deficiencies – simply separate supplements away from coffee by at least 2 hours.
Personally, I would recommend avoiding coffee when there is hair loss since more data illustrates its negative effects instead.
Biotin-rich foods like berries, liver, legumes, oily fish and bananas condition the skin and scalp creating an overall healthy environment for strong hair. Other foods to include in the diet are soybeans, pumpkin seeds. Black pepper, sesame seeds, and bone soup.
Iron-rich foods include dark-green leafy vegetables, brown rice, pulses and beans, nuts and seeds, white and red meat, fish, tofu, eggs, and dried fruit (such as dried apricots, prunes, and raisins). In particular, you should try to include foods and drinks containing vitamin C, as vitamin C can help your body to absorb iron. However, high levels of some foods and drinks, as well as certain medicines, may make it harder for your body to absorb iron. These include:
– tea and coffee
– calcium, found in dairy products such as milk
– antacids and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which are medications sometimes used to relieve indigestion
– whole-grain cereals – although whole grains are a good source of iron themselves, they contain phytic acid, which can stop your body from absorbing iron from other foods and pills
Folate is found in small amounts in many foods. Good sources include broccoli, Brussels sprouts, liver, spinach, asparagus, peas, chickpeas, brown rice, and fortified breakfast cereals
Good sources of vitamin B12 include meat, salmon, cod, milk, cheese, eggs, and some fortified breakfast cereals.
However, because vitamin B12 is not found in foods such as fruit, vegetables, and grains, vegans may not get enough of this vitamin.
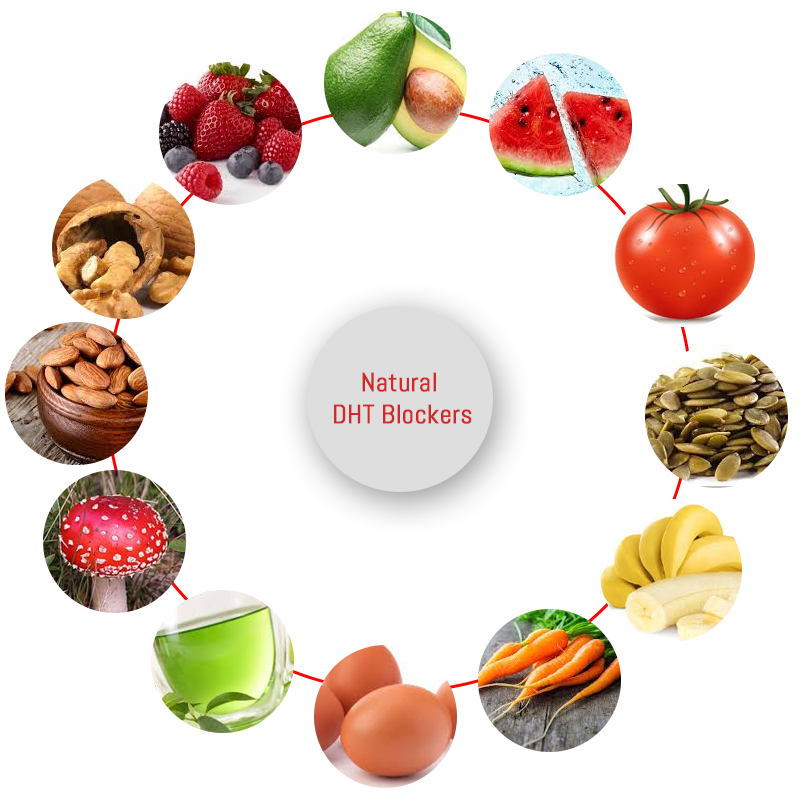
Lifestyle Changes
Practicing a healthy lifestyle can help reduce DHT levels naturally. This includes regular exercise, quitting smoking, reducing stress, taking time to rest/getting enough sleep, and doing scalp exercises like massages to reduce tension and increase blood flow.

Other Things To Consider
False Promises
There are numerous devices and products that are marketed as effective hair loss treatments, but many of them do not work. Beware of all of the false advertising associated with these products. If a cure for hair loss in women sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Before-and-after pictures may have been doctored to be misleading. How do you know if a hair loss treatment really works? Ask your dermatologist about any treatment you are considering.
Style Your Hair Right
Hairstylists are a great resource for help with hair loss in women. A new haircut or hairstyle may be just what you need to make your hair appear fuller. Ask your stylist for advice about getting a shorter cut, parting your hair in a different location, or adding curls or waves to add volume to your hair. Products for hair loss in women include using styling products designed for thin hair. Some products are added to the roots while hair is damp before blowing dry. Some cosmetic products can help disguise the appearance of bald spots. Ask your stylist or dermatologist for recommendations about the products and strategies that will work best for you.
Managing Major Hair Loss
There are many things you can do to disguise sudden hair loss in women that is severe. You can use a hat, scarf, or bandana to cover your head. If you have bald areas, consider getting a weave or concealing the bald area with a hairpiece. Wigs can be very natural-looking. They fit so well you can even wear them while you are working out at the gym or swimming. If hair loss causes severe distress and it is affecting your self-esteem or ability to carry out daily activities, seek the help of a therapist.
CLICK HERE to book a consult online.
**If you’ve got this far – thank you for reading and I look forward to bringing you more information in the future.
Now, for those interested in learning more about female hair loss enjoy this video:
